ISRO Space Farming Milestone: Cowpea Seeds Sprout In Orbit
On January 4, 2025, the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) declared the sprouting of cowpea seed in outer space, thus achieving a major milestone in agricultural research beyond Earth. This achievement was realized shortly after the PSLV-C60 SpaDeX mission, which launched on December 30, 2024, carrying 24 payloads, including the innovative PS4-Orbital Experiment Module (POEM-4).
Cowpea Seed Germination in Space
The CROPS (Compact Research Module for Orbiting Plant Studies) experiment, built by the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), has succeeded in sprouting cowpea seeds in merely four days. This experiment aims to examine plant growth in microgravity, something quite significant for future long-duration space missions. The ISRO space farming experiments involve growing eight seeds in a controlled and closed-box environment with active thermal management. The experiment is designed to be fully automated, to last between five to seven days, and to focus on the ability to demonstrate seed germination and support growth up to the two-leaf stage.
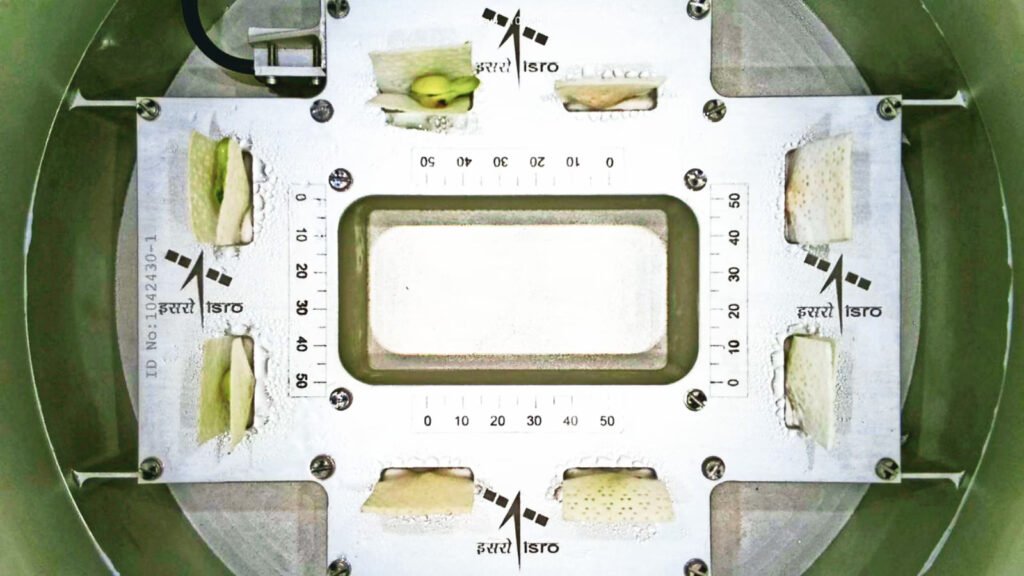
The Role of POEM
The PS4 Orbital Experiment Module (POEM) is a stabilized platform intended for performing various experiments in space. It has solar cells and a lithium-ion battery to power multiple payloads. Advanced navigation is provided by the sun sensors, gyros, and magnetometer. At POEM’s core is increased platform stability over the previous orbital experiment platforms, and this has translated into increased scientific capabilities for the experiments on board.
Importance of Crop Research In Space
Doing experiments in space in agricultural sciences is vital for future explorational flights. Studying plant growth in microgravity will help scientists find ways to sustain food supply for long-duration exploration mission astronauts. The CROPS experiment is one monophasic platform activated to develop ISRO’s ability to grow plants in deep space environments. Prosperous plant growth in space can support the life of other planets, paving the way for further colonization efforts.
Future Prospects In Space Exploration
By conducting successful experiments, India is setting precedents in space technology and research and, in the future, more advanced missions will be possible. Growing plants in the space environment and operating advanced robot systems will permit complex missions in the future. The ISRO will continue to innovate, given the relationship between these advances and studies in human existence away from Earth, such as the possibility of living sustainability on other planets.
ISRO’s Space Farming Experiments: The Cowpea Project
The cowpea (Vigna unguiculata), also known as the black-eyed pea, was chosen for ISRO’s experiment due to its resilience and nutritional value. Known for its adaptability to various climates and soil conditions, cowpea is a staple crop in many parts of India and Africa. This makes it an ideal candidate for space farming experiments.
During a recent space mission, cowpea seeds were sent aboard a satellite equipped with a controlled environment simulating essential Earth-like conditions, such as light and temperature. Scientists observed the seeds’ germination and early growth stages under microgravity.
The results were groundbreaking: the seeds not only germinated but also exhibited promising growth patterns. These findings provide valuable insights into plant biology in space and pave the way for further experiments involving other crops.
Why Space Farming Matters
ISRO’s success with ISRO space farming experiments is more than just a scientific feat; it holds the potential to revolutionize life beyond Earth. Here are some key implications:
- Sustainable Space Exploration: Growing food in space reduces dependency on Earth-based supplies, making long-term missions more feasible.
- Nutritional Security for Astronauts: Freshly grown crops can provide essential nutrients, improving astronauts’ health and well-being during extended space travel.
- Agricultural Innovations: The knowledge gained from space farming experiments could lead to breakthroughs in Earth-based agriculture, such as drought-resistant or high-yield crops.
Final Words
By successfully sprouting cowpea seeds in orbit, ISRO has demonstrated its commitment to pushing the boundaries of scientific research. This pioneering effort in space farming not only strengthens India’s position in global space exploration but also brings humanity one step closer to sustainable living in space. As ISRO continues its ISRO space farming experiments, the dream of cultivating lush green farms on the Moon or Mars is no longer a distant vision but a foreseeable reality.







