What Is Guillain Barre Syndrome? Know The Key Symptoms
Guillain Barre Syndrome (in brief, GBS) finds new dimensions in India’s Maharashtra, given that, as of January 26, 101 cases have been confirmed in Pune. A report filed by ANI described that this number is inclusive of 81 cases in the Pune Municipal Corporation (PMC) jurisdiction area, 14 in Pimpri Chinchwad, and 6 in the affected district. The number of men 68 cases and women’s figures at 33 show that 16 people are currently on ventilators. In distress, the death of one patient due to suspected GBS was reported from Solapur, Maharashtra. What is GBS syndrome, and what causes the condition? Dr. Aditya Gupta, Director- Neurosurgery & Cyberknife, Artemis Hospital, Gurugram, shares his knowledge.
In the Solapur district of Maharashtra, a patient suspected to have Guillain Barre Syndrome (GBS) died. The count of patients with disorders of the nervous system was above 100 in Pune. This is reportedly the first death from GBS in Maharashtra: The male aged 40 is a resident of Solapur, and he was in Pune, where it is suspected he picked it up. The Union health ministry has dispatched a special team to Sinhgad to study the city where GBS outbreak has occurred.
What Is Guillain Barre Syndrome?
Guillain Barre Disease is a rare case where the immune system attacks the body’s nerves. “The body will feel weak, and your hand might feel like experiencing needles. Sometimes, the patient feels that it will help to become paralyzed. The symptoms might start with a person’s feeling that he/she cannot get up easily. This usually occurs after an infection like flu or some stomach disorder?” says Gupta.
Symptoms Of GBS
Guillain Barre Syndrome (GBS) is a rare neurological disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its nerves. Although GBS is often associated with a history of recent viral infections, its exact cause remains unknown, says Dr. Gupta. He shares, “Even though specific vaccines have been reported to increase the risk of GBS, the benefits of these vaccines in preventing serious infections continue to outweigh the risk for GBS.” Symptoms can vary in severity and progression, but common signs include:
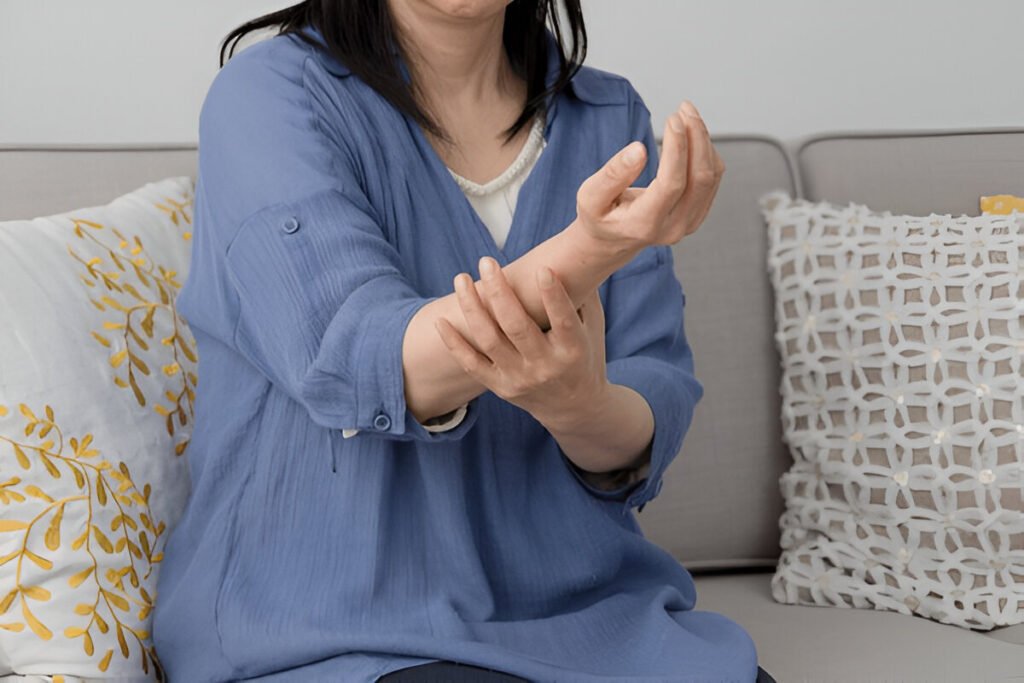


Early Symptoms:
- Tingling and Weakness
- Pins-and-Needles Sensation
- Muscle Weakness
Progressive Symptoms:
- Weakness may spread, potentially affecting breathing and facial muscles.
- Problems such as double vision or difficulty speaking, chewing, or swallowing.
- Sharp or cramp-like pain, often in the back or legs.
- Reduced or absent reflexes in the arms and legs.
- Difficulty maintaining balance or coordinating movements.
Severe Symptoms:
- Paralysis
- Difficulty Breathing
- Heart and Blood Pressure Issues
Additional Symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Difficulty with bladder or bowel control
- Tingling or numbness without weakness (less common)
How To Prevent GBS?
The state health department in an advisory shared that one can prevent GBS disease up to a certain extent by taking general precautions such as:
- 1. Reduce the Risk of Infections
- 2. Stay Up-to-Date with Vaccinations
- 3. Seek Prompt Treatment for Infections
- 4. Avoid High-Risk Areas for Zika Virus
- 5. Understand Personal Risk Factors
- 6. Avoid Unnecessary Medical Procedures
Types of Guillain Barre Syndrome
GBS can manifest in different forms, including:
- Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (AIDP): The most common type, characterized by muscle weakness that starts in the lower body and ascends.
- Miller Fisher Syndrome (MFS): A rarer form that primarily affects the eyes and is associated with an unsteady gait.
- Acute Motor Axonal Neuropathy (AMAN) and Acute Motor-Sensory Axonal Neuropathy (AMSAN): These subtypes are more common in certain regions, such as Asia and Latin America.
Diagnosis And Treatment
If GBS is suspected, a healthcare provider may perform a physical examination and recommend tests such as:
- Lumbar Puncture: To check for elevated protein levels in cerebrospinal fluid.
- Electromyography (EMG): To assess nerve activity and detect abnormalities.
- Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS): To measure the speed of electrical signals in the nerves.
Treatment options aim to reduce the severity of the disease and accelerate recovery. These include:
- Plasma Exchange (Plasmapheresis): Removes harmful antibodies from the blood.
- Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG): Provides healthy antibodies to neutralize the harmful ones.
- Supportive Care: This may involve physical therapy, pain management, and respiratory support in severe cases.
Stay up to date on all the latest news, and follow all the important information and details in 360Infoclub.
Reference Link:
https://www.ndtv.com/india-news/ndtv-explainer-symptoms-of-guillain-barre-syndrome-and-how-to-prevent-it-7573284
https://indianexpress.com/article/cities/pune/weakness-in-legs-could-not-get-up-patients-their-families-on-guillain-barre-syndrome-9802551/
https://zeenews.india.com/health/guillain-barre-syndrome-claims-life-in-maharashtra-what-causes-it-symptoms-know-all-about-gbs-2849469